Arthroscopic Shoulder Stabilisation
How Is Arthroscopic Shoulder Stabilisation Performed?
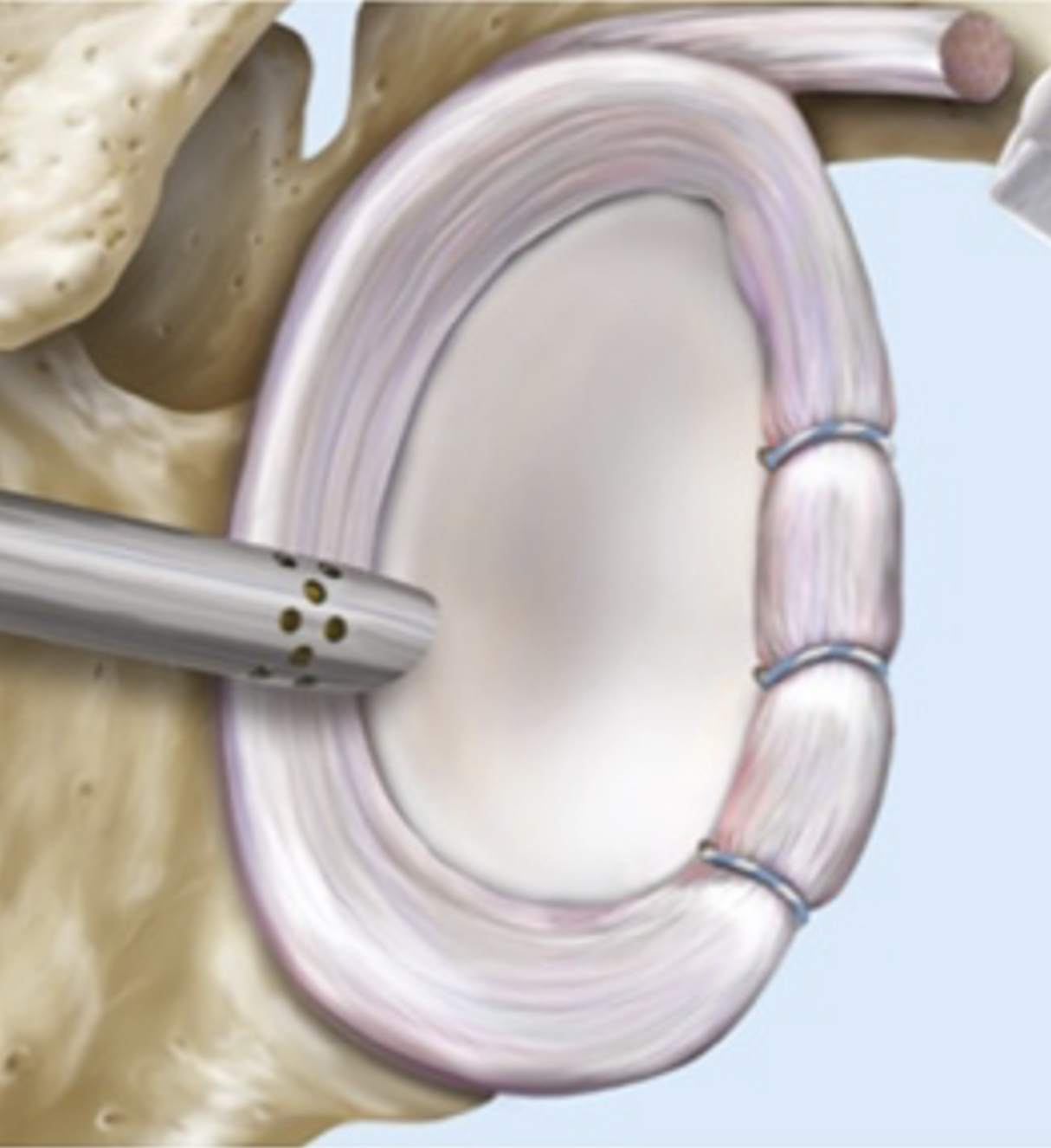
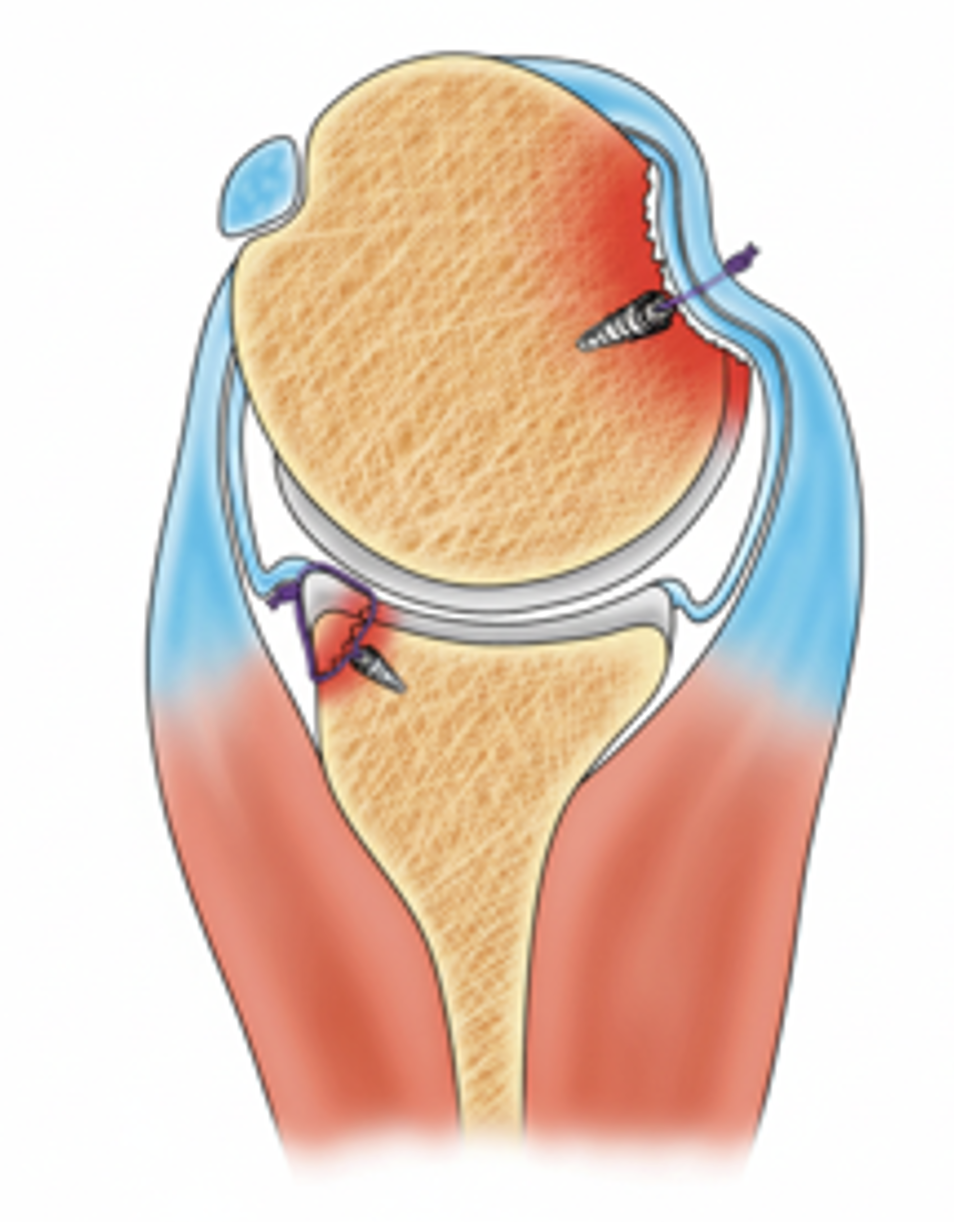
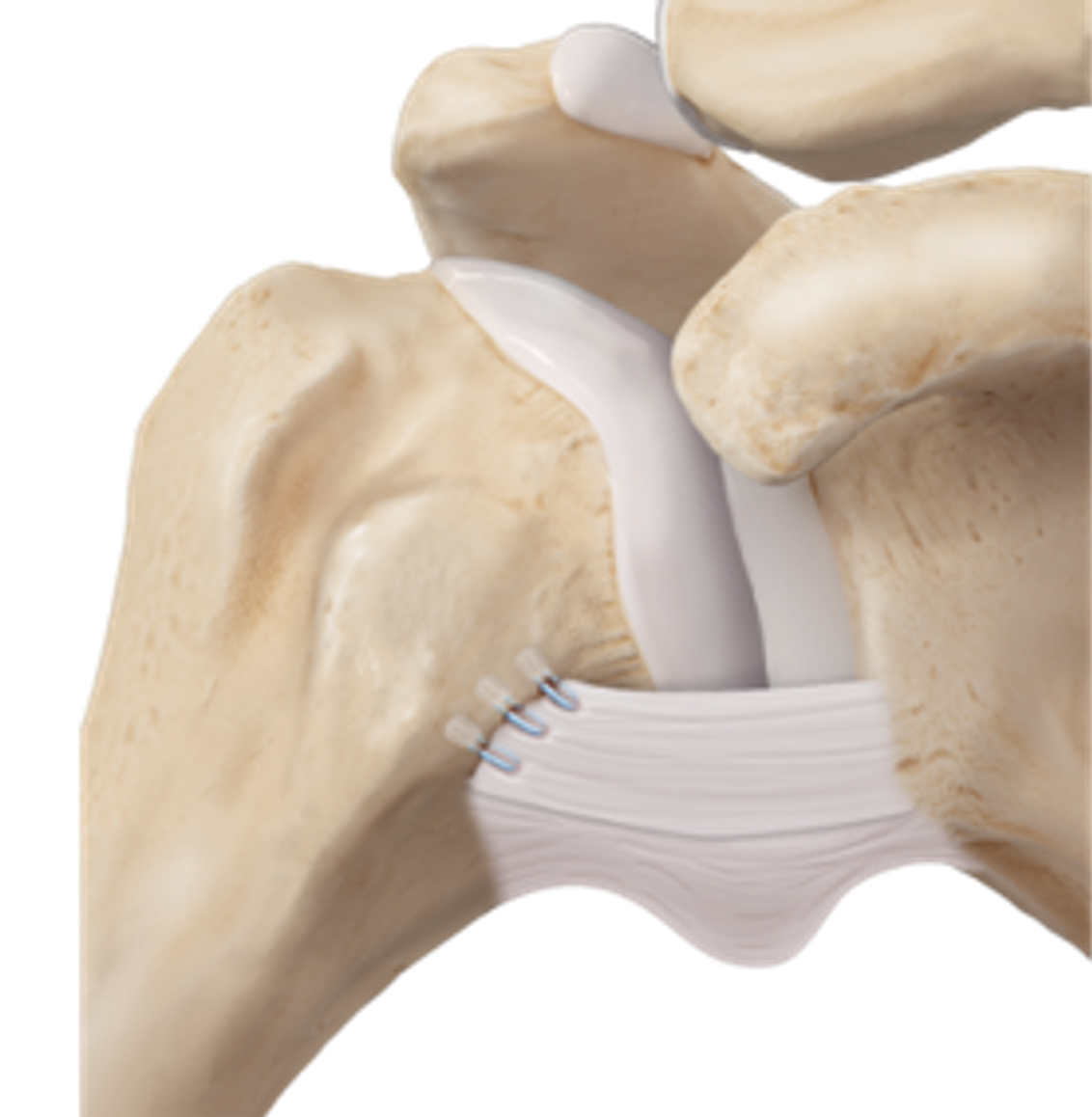
Arthroscopic shoulder stabilization is a minimally invasive procedure performed to restore stability to the shoulder joint after recurrent dislocations or instability. Small incisions are made around the shoulder to insert a camera (arthroscope) and specialized instruments. The torn labrum and capsule are repaired using sutures and small anchors to reattach the soft tissues to the bone. In some cases, capsular tightening or bone augmentation procedures may also be performed depending on the degree of instability and tissue damage. The goal is to restore normal anatomy and prevent future dislocations while maintaining shoulder motion and function.
What Is the Recovery in the Immediate Postoperative Period?
Hospital stay: Most patients stay 1 day in hospital to recover and review pain control and physiotherapy instructions.
Sling: You will wear a sling to protect the shoulder for 4–6 weeks.
Range of motion: Passive shoulder motion is started under physiotherapist supervision. Active movement and strengthening begin progressively over the following weeks.
Ice: Used frequently to control pain and swelling. You should ice for 20 minutes, 3–4 times per day immediately after surgery. An ice/compression machine can be hired from a third party.
Sleep: You may find it more comfortable to sleep in a reclined or semi-upright position with the sling on for the first few weeks.
How Is the Wound Managed?
Bulky dressings will be removed 1–2 days after surgery.
A waterproof underlay dressing should be left on for 1–2 weeks.
Incisions typically heal within 2 weeks.
Showers are permitted while wounds are covered with waterproof dressings during the first 2 weeks.
Do not submerge incisions in water (baths, pools, or ocean) for 4 weeks.
A wound check with your GP, allied health provider, or our clinic is recommended at 2 weeks.
Absorbable sutures are usually used and do not require removal, though small remnants may surface naturally during healing.
How Do I Manage My Pain After Arthroscopic Shoulder Stabilization?
Your anaesthetist may use a regional nerve block to help control pain for the first day of your recovery.
Local anaesthetic will also be injected into the shoulder during the procedure.
Use ice regularly (20 minutes, 3–4 times per day). An ice machine may be hired from a third party.
Take prescribed pain medication as directed. Opioids may be used short-term but have known side effects (nausea, constipation, dependence). Non-opioid medications such as paracetamol or anti-inflammatories are preferred when tolerated.
Keep the arm supported in the sling to reduce strain on the repaired tissues and decrease pain.
What Issues Should I Call the Clinic Regarding?
You should contact your surgeon or clinic immediately if you notice:
Increasing redness, swelling, or foul-smelling drainage from the wound.
Persistent or worsening pain not controlled by medication.
Fever, chills, or night sweats.
Numbness or tingling that does not resolve after the nerve block wears off.
Any acute reinjury to your operative shoulder.
Prompt review allows early management of potential complications.
When Can I Return to Normal Activities After Arthroscopic Shoulder Stabilization?
Recovery time varies depending on the type of repair and your individual progress. As a general guide:
Light daily activities: Immediately, using your non-operated arm.
Desk or computer work: 1–2 weeks, if comfortable.
Progressive shoulder strengthening: Begins around 6–8 weeks under supervision.
Return to contact or overhead sports: Typically 6–9 months after surgery, depending on recovery and the nature of the sport.
When Can I Drive?
You can usually drive once you can safely control the steering wheel and perform emergency maneuvers comfortably. This is typically around 6–8 weeks postoperatively. You must not drive while taking strong pain medication (e.g., opioids).
When Can I Return to Work?
Return to work depends on your occupation:
Office or sedentary work: 1–2 weeks, once you can safely commute and perform desk duties with the sling.
Light manual work: 6–8 weeks.
Heavy manual labour or overhead work: 3–4 months or longer, depending on recovery and surgeon clearance.
Should I See a Physiotherapist?
While not necessary, formal physiotherapy is strongly recommended for optimal recovery after arthroscopic shoulder stabilization. Your physiotherapist will:
Guide you through a staged rehabilitation program focusing on gradual range of motion, strength, and shoulder control.
Emphasise scapular stability and safe return to sport-specific movements.
Help monitor healing progress and modify activities accordingly.
Most patients continue physiotherapy for 4–6 months, with full recovery and return to sport typically achieved around 6–9 months.
What Are the Complications After Arthroscopic Shoulder Stabilization?
While complications are uncommon, they may include:
Recurrent instability or redislocation.
Shoulder stiffness or loss of motion.
Infection or wound healing issues.
Nerve injury or irritation (usually temporary).
Anchor or suture-related irritation.
Persistent pain or weakness.
Progression of arthritis in the shoulder.
Inability to return to sport/activities or perform at the same level.
Complications from anaesthetic block (pneumothorax, nerve toxicity, shortness of breath from phrenic nerve involvement).
Fracture